What is vertical farming and what are its advantages? We can say that it is one of the most innovative farming methods of the modern age. This system allows plants to be grown vertically rather than horizontally. This enables high yields even in limited spaces. In today’s world of rapidly increasing urbanization, vertical farming is an important solution that makes food production sustainable.
This method uses water-based nutrient solutions, special LED lights, and automation systems instead of soil. This allows for year-round production, independent of outdoor weather conditions. Vertical farming offers opportunities for both small-scale entrepreneurs and large producers. Moreover, this model, seen as the future of agriculture, also contributes to the efficient use of natural resources.
In this article, we will examine in detail how vertical farming works, the systems used, its advantages, and its technological infrastructure. We will also discuss its relationship with urban farming and its economic and environmental impacts. At the end of the article, you will find predictions about how vertical farming could transform the future.
Contents
- Definition and Basic Principles of Vertical Farming
- Types of Vertical Farming Systems
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Vertical Farming
- Technologies Used in Vertical Farming
- The Impact of Vertical Farming on Urban Agriculture and Sustainability
- Considerations for Setting Up Vertical Farming
- The Economic and Social Contributions of Vertical Farming
- The Future of Vertical Farming and New Trends
- FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Definition and Basic Principles of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is an agricultural method in which plants are grown in stacked layers. This system makes it possible to produce crops in limited spaces, especially in cities. While traditional farming requires large areas of land, vertical farming only needs a few square meters.
How does vertical farming work?
In this method, plants are grown on special shelving systems. Water and nutrients are automatically distributed to each layer. Lighting is provided by LED systems. These lights are adjusted to the wavelengths required by plants for photosynthesis. This increases productivity and improves product quality.
Differences from traditional farming
Vertical farming uses hydroponic, aeroponic, or aquaponic systems instead of soil. It does not require working with soil, and harmful insects are seen at a minimum level. In addition, production continues 12 months a year. Up to 90% less water is used compared to traditional farming.
Mini summary: Vertical farming is a space-saving, highly productive, and environmentally friendly production method. It forms the basis of sustainable agriculture by conserving natural resources.
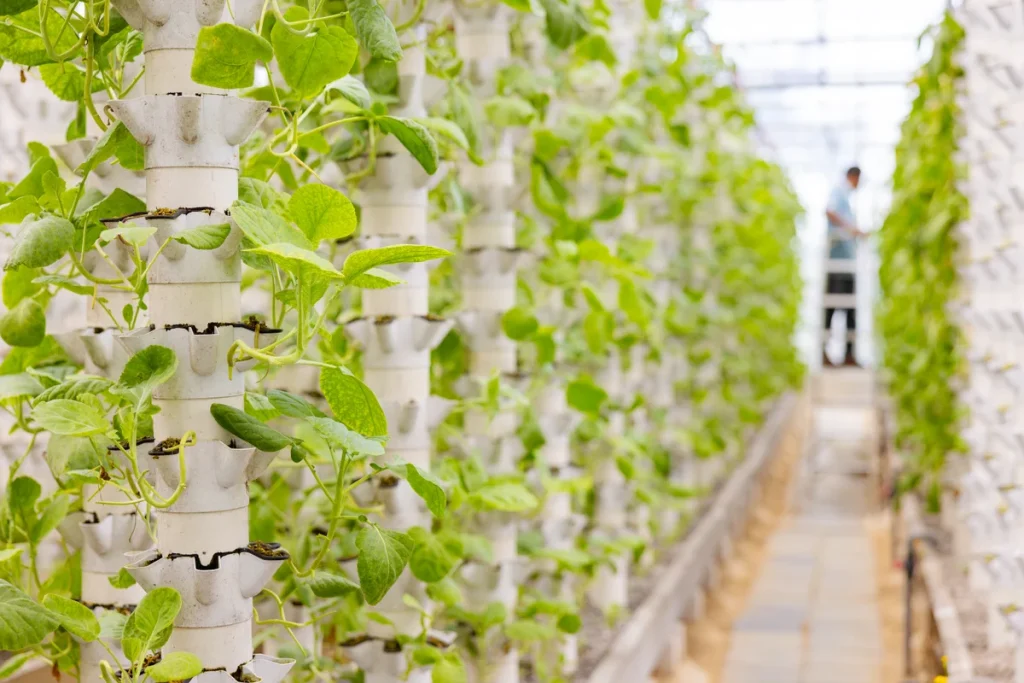

Types of Vertical Farming Systems
The systems used in vertical farming vary according to different needs. The most common models include hydroponic, aeroponic, and aquaponic systems. Each offers different advantages in terms of water, nutrient, and energy management.
Hydroponic system
In this system, plants are fed with nutrients dissolved in water. No soil is used. Water circulates in a closed loop, preventing water waste. Hydroponic systems are particularly effective for high yields of leafy greens.
Aeroponic system
In an aeroponic system, plant roots are suspended in the air. Nutrient solutions are sprayed in mist form. This method allows the roots to receive maximum oxygen. As a result, plants grow faster.
Aquaponic system
An aquaponic system combines fish farming with plant production. Fish waste is recycled as nutrients for plants, and plants purify the water and return it to the system. This cyclical structure offers an environmentally friendly solution.
Mini summary: Hydroponic, aeroponic, and aquaponic systems are the cornerstones of vertical farming. Each offers different advantages, optimizing resource use.
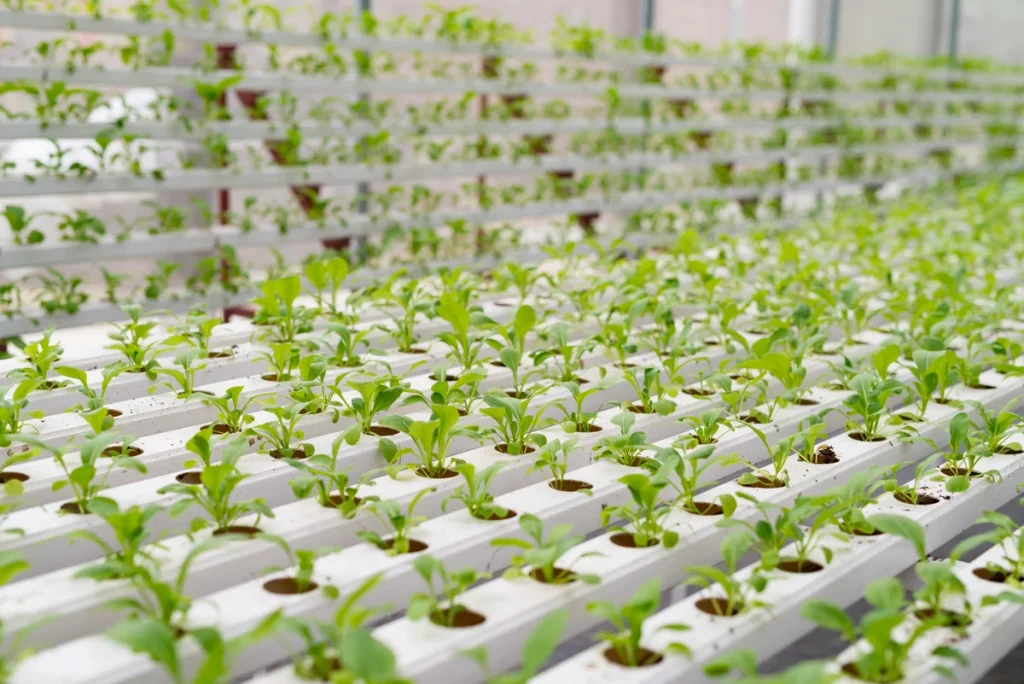

Advantages and Disadvantages of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming has many advantages. Most importantly, it offers the possibility of production in areas with limited agricultural land. In addition, production is not affected by outdoor weather conditions. However, as with any technology, there are some disadvantages.
Water and energy efficiency
Vertical farming uses 90% less water than traditional methods. Water is recycled in this system. LED lighting saves energy. This protects the environment and reduces production costs.
Continuous production and space savings
Vertical structures allow year-round production even in limited spaces. Climate conditions do not affect production. However, initial investment costs are high. This can pose a challenge for small-scale ventures.
Mini summary: Vertical farming offers significant advantages in terms of water savings and efficiency. However, high installation costs and the need for technical knowledge can be considered disadvantages.
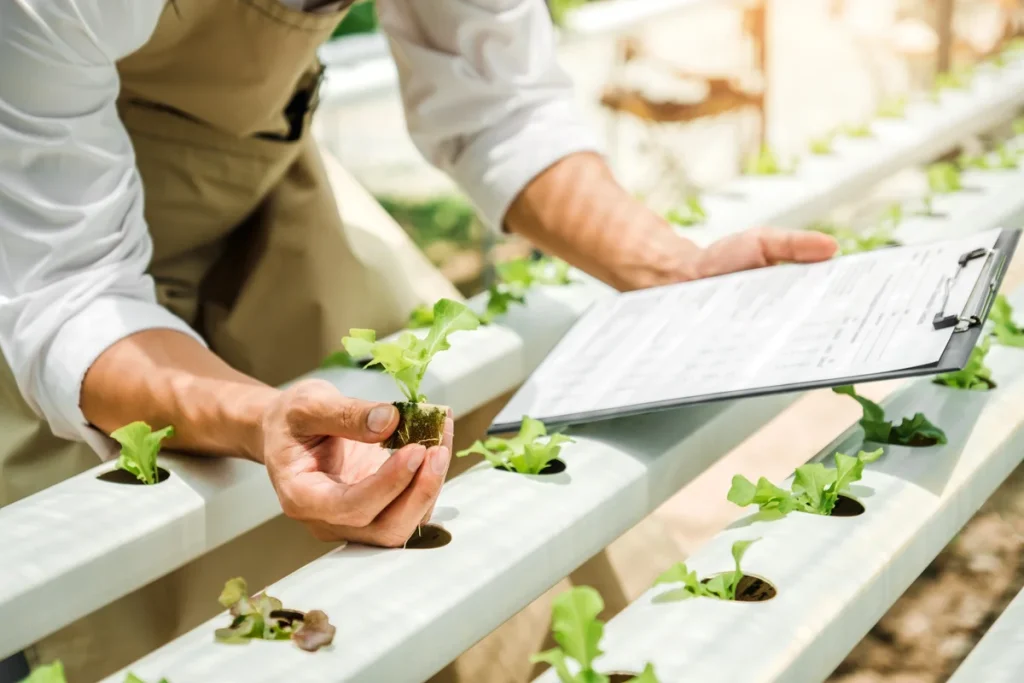

Technologies Used in Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is one of the areas where technology is most intensively integrated into agriculture. These systems utilize sensors, automation tools, and artificial intelligence-powered analytics. This ensures that each plant’s needs are met at the right time.
Sensors and IoT Applications
Humidity, temperature, pH, and nutrient values are continuously monitored with sensors. IoT-based systems analyze this data. Operators can adjust environmental conditions using a remote control panel. This minimizes production errors.
The role of artificial intelligence and automation
Artificial intelligence optimizes irrigation and nutrient distribution based on data analysis. It also predicts harvest time. Automation reduces labor requirements and increases efficiency. Technology makes production processes more sustainable.
Mini summary: Sensors, IoT, and artificial intelligence form the heart of vertical farming. These technologies prevent resource waste and make production smarter.
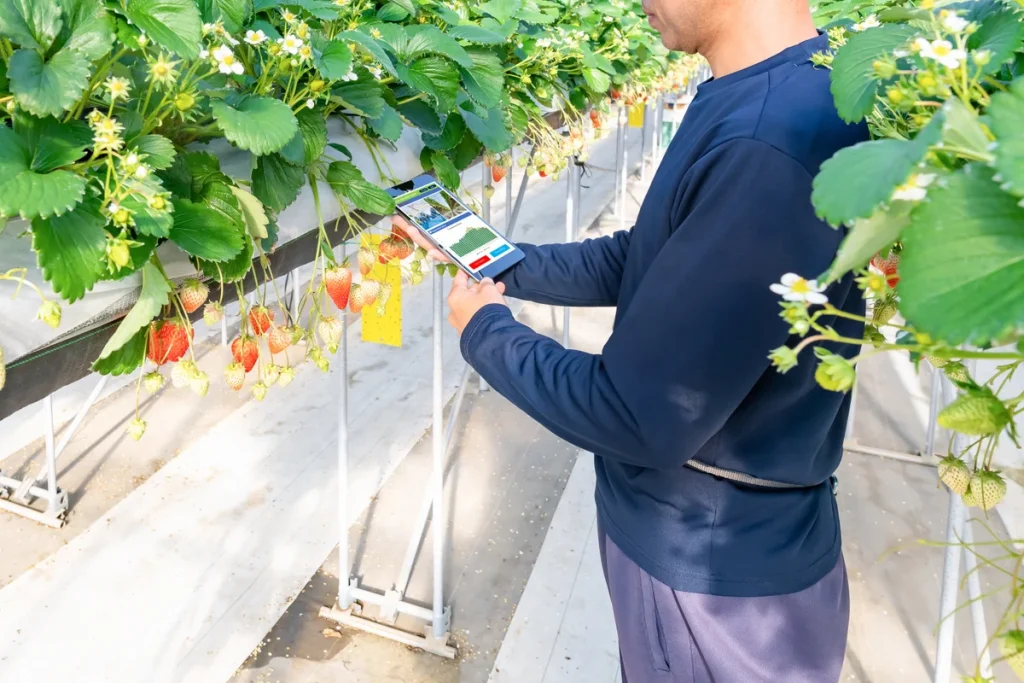

The Impact of Vertical Farming on Urban Agriculture and Sustainability
Vertical farming is an important innovation that enables food production despite growing populations in cities. As traditional farming areas decrease due to urbanization, vertical systems can be installed inside buildings or on rooftops. This makes it possible to grow fresh produce even in city centers.
Food production in urban areas
Vertical farming supports local production. Food reaches the table quickly from where it is produced. This reduces both transportation costs and carbon emissions. People living in cities can consume fresher products from local producers. This system also provides a solution to the issue of “food security” in cities.
Reducing the carbon footprint
Vertical farming contributes to the environment by reducing fossil fuel consumption. Reduced transportation, water recycling, and limited use of chemical fertilizers minimize the carbon footprint. This method supports the creation of sustainable cities.
Mini summary: Vertical farming enables food production in cities and reduces carbon emissions. This represents an important step towards sustainable urban living.

Key Considerations for Vertical Farming Setup
Setting up a vertical farming system requires careful planning. Environmental conditions, energy usage, and plant species must be taken into account for a successful setup. At this stage, choosing the right technology and system is critical.
Light, water, and nutrient balance
LED lights play an important role in the photosynthesis process of plants. Light intensity and color should be adjusted according to each plant species. The water and nutrient mixture should be controlled with sensitive sensors. Otherwise, plant growth will be negatively affected.
Suitable environmental conditions
Vertical farming systems are usually set up in closed environments. Therefore, temperature, humidity, and air circulation must be carefully managed. In addition, energy-efficient equipment should be preferred. This both reduces costs and increases sustainability.
Mini summary: For a successful vertical farming system, the right balance of light, water, and environment must be established. A planned setup ensures high yield in the long term.
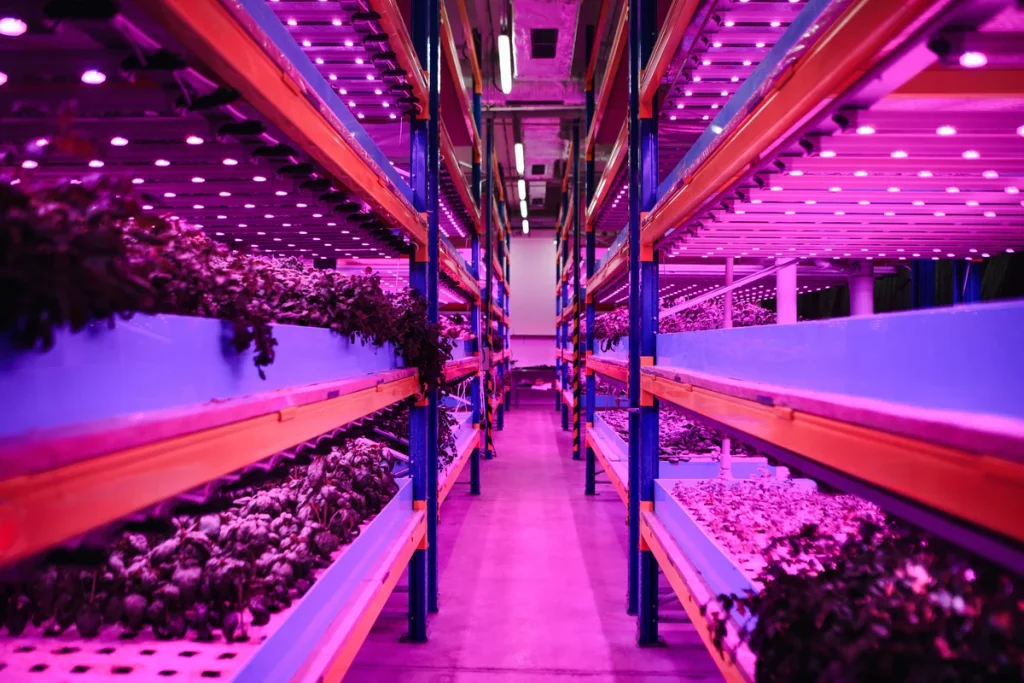

The Economic and Social Contributions of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming has significant impacts not only environmentally but also economically and socially. This system creates new employment opportunities and contributes to the local economy. It also strengthens food security.
Local employment opportunities
Vertical farming facilities established in cities create employment in many areas, from production to harvesting. The combination of agriculture and technology increases the interest of the young population in this sector. Thus, agriculture becomes an attractive profession again.
Contribution to food security
Vertical farming reduces the need for pesticides thanks to controlled production. Products are fresh, clean, and high in nutritional value. This directly impacts public health. It also strengthens the local food supply by reducing dependence on imports.
Mini summary: Vertical farming increases employment, revitalizes the local economy, and supports food security. It thus contributes to sustainable development.

The Future of Vertical Farming and New Trends
As technology advances, the potential of vertical farming also increases. Artificial intelligence, data analytics, and automation systems could completely transform agriculture in the future. Innovative projects such as space farming are also part of this transformation.
Smart farms
Smart farms optimize production processes by analyzing sensor data. In these systems, each plant is monitored individually. Automated irrigation, fertilization, and light control increase efficiency. In the future, these farms are expected to become widespread in cities.
Space farming and innovations
Space agencies are testing vertical farming systems for use in space missions. The basic principles of growing plants in zero-gravity environments are studied using this method. This research also inspires agricultural practices on Earth.
Mini summary: The future of vertical farming is being shaped by smart technologies and innovations. These systems will enable sustainable production both on Earth and in space.

FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Vertical farming is an agricultural method where plants are grown in stacked layers without using soil. This system allows for high yields even in limited spaces.
It is ideal for fast-growing plants such as lettuce, spinach, basil, strawberries, and tomatoes. High yields are generally achieved with leafy vegetables.
The initial setup cost is high, but it pays for itself in the long run through energy and water savings.
No. Instead of soil, nutrient solutions dissolved in water or mist are used in vertical farming systems.
It enables environmentally friendly production through water savings, reduced carbon emissions, and decreased chemical use.
Yes. The interiors of buildings, rooftops, or empty warehouses are suitable for vertical farming. This allows for the production of fresh food within cities.
Water, light, and nutrient control are automatically managed through sensors and IoT technologies.
With artificial intelligence and smart farm systems, vertical farming will become widespread in the future. Its use is even planned for space missions.
It is profitable in the long term. Especially in city centers, the profit potential is high due to low logistics costs.
Energy usage is optimized thanks to LED technologies. When supported by renewable energy sources, consumption is minimized.
Vertical farming is the sustainable agriculture model of the future. You too can contribute to the environment and local economy by setting up your own vertical farming system.

 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 ქართული
ქართული
 العربية
العربية








